List of Root Procedure for Huawei MA5671A
For documentation purposes only. This page contains the history of root procedures for the Huawei MA5671A stick.
Root Procedure for Huawei MA5671A (V3 - Web serial)
Can be accessed via the link Web root procedure
Root Procedure for Huawei MA5671A (V2 - Python)
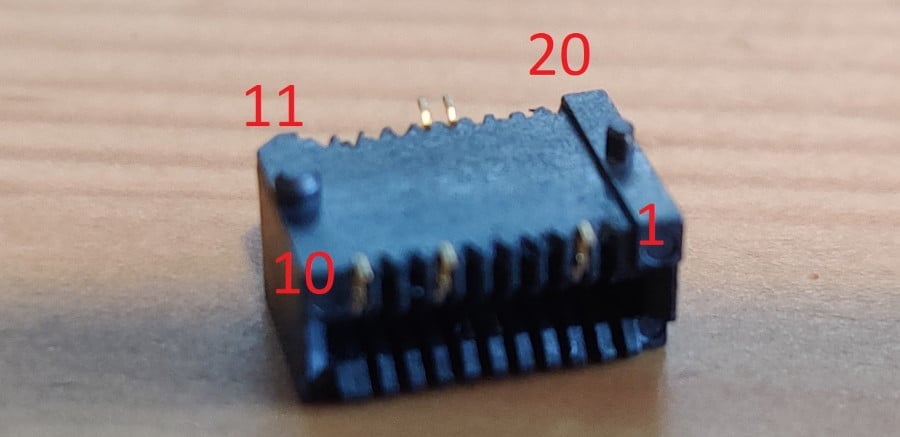
- Take the SFP molex and four coloured cables and solder them to the molex according to the following diagram:
| USB TTL (UART) Adapter | wire colour in picture | SFP 20pins Molex connector |
|---|---|---|
| 3.3V | red | pin #15 and #16 |
| TX | orange | pin #2 |
| RX | yellow | pin #7 |
| GND | green | pin #14 |
- Install python and
pyserialwithpippip install pyserial - Make the connections as shown to a TTL adapter except for GND (which should remain detached as it is used as a switch)
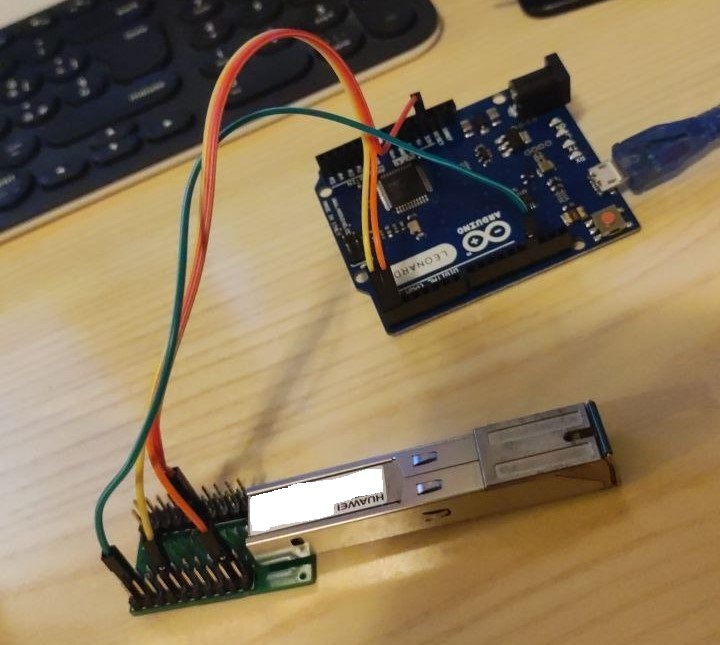


- Open Tera Term (or other serial terminal emulators), find the correct serial port of the TTL adapter, change the port on the script on line 7 instead of
COM8. - After this, run the following python script and connect the GND pin:
import sys
import time
import serial.tools
try:
ser = serial.Serial("COM8", 115200, parity=serial.PARITY_NONE, stopbits=serial.STOPBITS_ONE, bytesize=serial.EIGHTBITS)
print('[+] Use serial port device:', ser.name)
print('[+] Waiting for trigger characters...')
while True:
try:
recv = ser.readline().decode()
except Exception as x:
print("Decode errore", x)
continue
if recv.startswith('U-Boot'):
print('[+] Received! transfer enable command...')
print('[+] Transfer command sequence 1')
t_end = time.time() + 3
while time.time() < t_end:
ser.write(chr(3).encode())
time.sleep(1)
print('[+] Transfer command sequence 2')
ser.write('setenv bootdelay 3\n'.encode())
time.sleep(1)
print('[+] Transfer command sequence 3')
ser.write('setenv asc0 0\n'.encode())
time.sleep(1)
print('[+] Transfer command sequence 4')
ser.write('setenv preboot "gpio set 3;gpio input 2;gpio input 105;gpio input 106;gpio input 107;gpio input 108"\n'.encode())
time.sleep(1)
print('[+] Transfer command sequence 5')
ser.write('saveenv\n'.encode())
time.sleep(3)
print('[+] Transfer command sequence 6')
ser.write('reset\n'.encode())
print('[+] Enable command transfer complete! rebooting...')
break
else:
print(recv)
except Exception as e:
try:
print('[!] Error:', e)
sys.exit(1)
finally:
e = None
del e
except (KeyboardInterrupt, SystemExit):
ser.close()
sys.exit(1)
setenv preboot: gpio input 105;gpio input 106;gpio input 107;gpio input 108;gpio set 3;gpio set 109;gpio set 110;gpio clear 423;gpio clear 422;gpio clear 325;gpio clear 402;gpio clear 424 - Reboot the stick
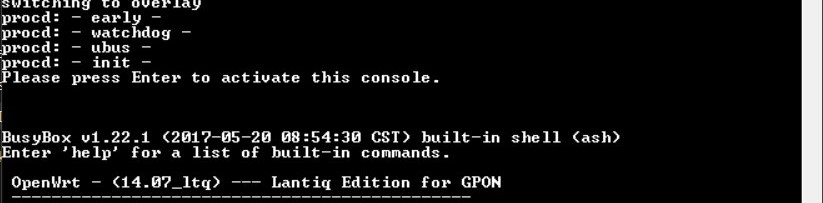
- Open Tera Term (or other serial terminal emulators), after it has loaded press
enterto activate the console
- With
sedchange the default shell from/opt/lantiq/bin/minishellto/bin/ashby editing the file/etc/passwd:
sed -i "s|/opt/lantiq/bin/minishell|/bin/ash|g" /etc/passwd
vim! [ 34.612000] Kernel panic - not syncing: Fatal exception in interrupt
[ 34.612000] Rebooting in 3 seconds..
- After this is done, reboot the stick, after connecting it to the router via an ethernet mediaconverter or directly plug it in an SFP port, with the port’s IP set to whatever IP of the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet (the stick has the IP 192.168.1.10)
- Run the terminal and login to the stick with ssh
ssh root@192.168.1.10
The password is admin123.
ssh -oKexAlgorithms=+diffie-hellman-group1-sha1 -oHostKeyAlgorithms=+ssh-dss [...] Root Procedure for Huawei MA5671A (V1 - Tweezers)
- take the SFP molex and the 4 coloured cables and solder them to the molex according to the following diagram:
| USB TTL (UART) Adapter | wire colour in picture | SFP 20pins Molex connector |
|---|---|---|
| 3.3V | red | pin #15 and #16 |
| TX | orange | pin #2 |
| RX | yellow | pin #7 |
| GND | green | pin #10 |


- Disassemble the stick by releasing the metal tabs that hold the cover in place. There are two tabs, one on each side, inside these holes:

-
Once you have removed the metal casing, you are left with the half-naked stick (note that the release mechanism also comes off easily and then you don’t know how to put it back together, so take a photo and memorise the positioning well).
-
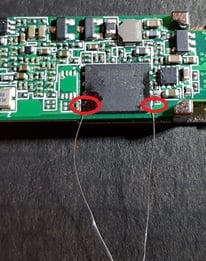
Before shorting the stick, connect the previously soldered cables and molex to the USB serial (photo immediately below) and to the stick (the molex, of course) and check that the jumper on the usb key is set to 3.3V

- The disassembled stick will appear as in the photo, in which I have highlighted in red the 2 pins to be shorted. Here they use wire, but a pair of tweezers is sufficient (I used those, in fact). Be careful not to make any other contacts by possibly covering everything else with electrical tape.



-
For the moment connect all cables to the usb key except the green (ground) or red (voltage), otherwise the stick will boot before you can do the following (N.B. for those who bought the uart above RX and TX are reversed). Open and configure Teratem for serial connection (select the correct com port, speed 115.200, english language, otherwise in japainise you can’t read anything understandable) insert the key in the PC (I take it for granted that it has already been installed, drivers and all), short the 2 pins seen above and keeping the short connected the missing coloured cable
-
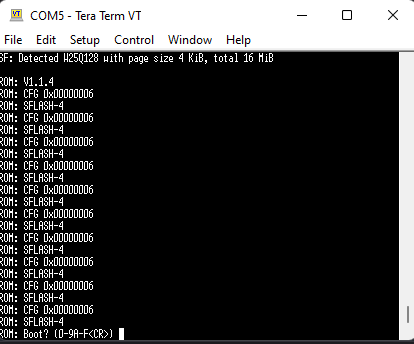
If you have done everything correctly, you should see something similar to the picture below (if nothing happens, you have obviously done something wrong with cables, molexes, soldering irons, etc., so you will have to start from the beginning again and work out which step you did wrong):
- Remove the short (tweezers or whatever you used), then type 7 and enter. You should see this:
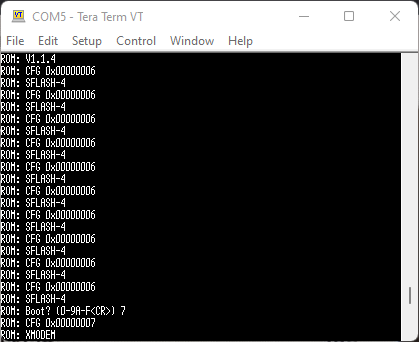
- From the Teraterm menu
FILE→TRANSFER→XMODEM→SEND→[1224abort.bin](which is the third of the files downloaded earlier):
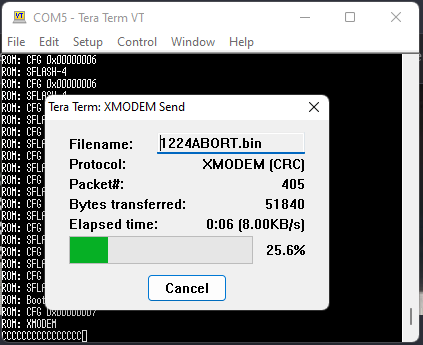
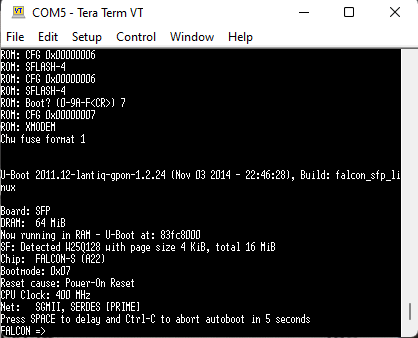
- As soon as the file transfer is complete, you have 2 seconds to press
CTRL+C, if you have not done so, you can return to the step 6. Otherwise, you should see:
- To permanently unlock the bootloader, without having to repeat the previous steps, you must give the following commands:
FALCON => setenv bootdelay 5 FALCON => setenv asc0 0 FALCON => setenv preboot "gpio set 3;gpio input 100;gpio input 105;gpio input 106;gpio input 107;gpio input 108" FALCON => saveenv
setenv preboot: gpio input 105;gpio input 106;gpio input 107;gpio input 108;gpio set 3;gpio set 109;gpio set 110;gpio clear 423;gpio clear 422;gpio clear 325;gpio clear 402;gpio clear 424 sed command documented in V2 - If you have done everything correctly you can reboot the stick (actually if you are convinced that everything is ok you could also close it again), disconnecting and reconnecting one of the 2 cables from before (ground or voltage), then again from the terminal you will have 5 seconds to lock the bootloader by doing a simple CTRL+C. Now upload the firmware image of the first mtd2 partition to the stick with the command
FALCON => loadb 0x80800000At this point it will appear:
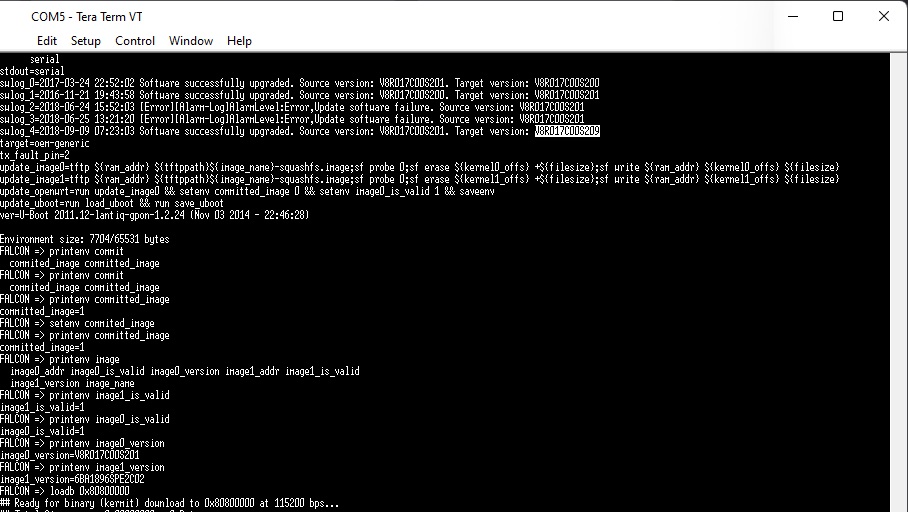
-
From the teratem menu do
FILE→TRANSFER→KERMIT→SEND→[mtd2.bin]. It will start uploading the file at a speed of about 3-4 KBps. Now you will have to wait more than half an hour for the upload to complete. - Once finished, the image loaded on the stick must also be saved to the corresponding system partition (the first of the 2) with the commands
FALCON => sf probe 0 FALCON => sf erase C0000 740000 FALCON => sf write 80800000 C0000 740000 - check that the stick is configured to boot from partition 0 (yes I know mtd2 goes on 0 and mtd5 goes on 1, complain to Laniq) with the command
FALCON => printenv committed_image - If it is 0, fine, otherwise configure partition 0 with the commands, and check if are 0.
FALCON => setenv committed_image 0 FALCON => saveenv FALCON => printenv committed_image
Miscellaneous Links
- Come avere i 2.5 Gbps su un unico dispositivo senza il Fastgate
- Support MA5671A SFP GPON
- La fibre Orange à 2Gbps, sur un routeur MikroTik 10Gbps CCR2004, via un ONT SFP+
- Bypassing the HH3K up to 2.5Gbps using a BCM57810S NIC